Python Programming Language
Start with Basics
——————————–
Python Language, created by Guido Van Rossum in 1989, is one of the high-level programming languages as of this era. First release of python Language in 1991. It has very simple easy-to-use syntax, creating it the proper language for someone trying to learn computer programming for the first time. For those of you aware of Java or C++, Python can break the myth you have got designed for a typical programing language. In this article, we will learn Python Programming language in the following topics:———————–
Why Learn Python Programming Language?
Python is a high-level programming language. It is very simple to learn and provides powerful typing. Python code has a very ‘natural’ style to it, in that it is easy to read and understand (thanks to the Python programming Language lack of semicolons and braces). The Python programming language works on any platform, from Windows to Linux to Macintosh, Solaris, and so on. The following Features of Python Programming Language.- Highly readable language
- Clean visual layout
- Less syntactic exceptions
- Superior string manipulation
- Elegant and dynamic typing
- Interpreted nature
- Ideal for scripting and rapid application
- Fit for many platforms





—————————-
Learn Python Programming | Python Programming – Step by Step
———————
Python Installation
Let us now move on to installing Python on a Windows systems.- Go to the link:https://www.python.org/downloads/ and install the latest version on your machines.

Figure: – Downloading Python programming Language
2. Download and install PyCharm IDE. Click –> here to download Pycharm IDE
Figure: Downloading PyCharm
PyCharm is an integrated development environment (IDE) used in computer programming, especially for Python programming languages. It provides code analysis, a graphical computer program. PyCharm is cross-platform, with Windows, macOS and UNIX versions————————-
Python Fundamentals
These are following the five fundamentals required to master Python:- Datatypes
- Flow Control
- Functions
- File Handling
- Object & Class
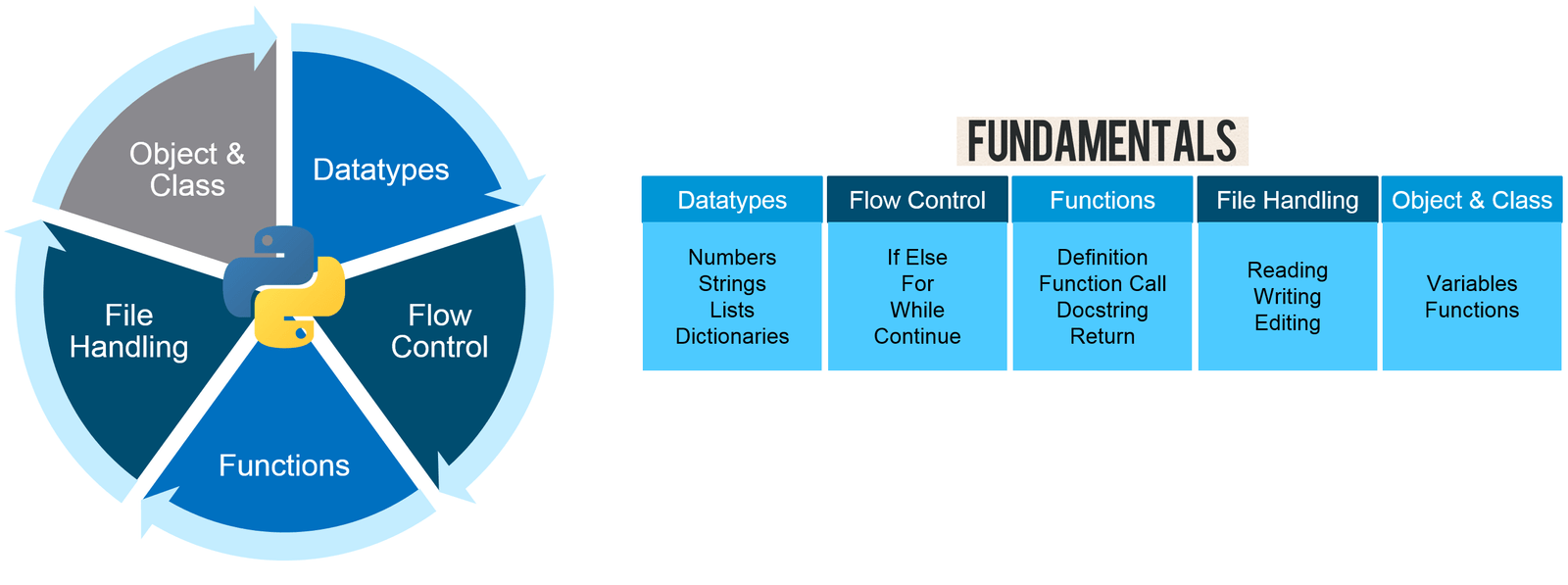
Figure: Python Programming Language- Fundamentals
1. Datatypes
All data values in Python are represented by objects and each object or value has a datatype.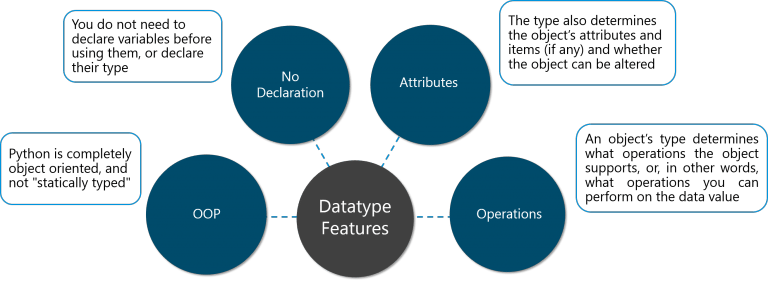
Figure: Python Programming Language – Datatype Features
There are eight native datatypes in Python Programing Language.- Boolean
- Numbers
- Strings
- Bytes & Byte Arrays
- Lists
- Tuples
- Sets
- Dictionaries

Figure: Python Programming Language – Native Datatypes
2. Flow Control
Flow Control helps us to understand the execution flow of our program. Let us take a Real–world example to understand this transformation. For this you need to control the execution of your Python program statements using Flow Controls.
- If
- For
- While
- Break
- Continue
- Pass
If Statement
The Python compound statement ’if’ lets you conditionally execute blocks of statements. Syntax of If statement:if expression: statement (s) elif expression: statement (s) elif expression: … else: statement (s)

Figure: Python Programming Language – If – Facebook Login Example
The above image explains the use of ‘if’ statement using an example of Facebook ID login. 1.Facebook login page will direct you to two pages based on whether your username and password is a match to your Facebook account. 2.If the Facebook password entered is wrong, it will direct you to the page on the left. 3.If the Facebook password entered is correct, you will be directed to your homepage. Let us now look at how Facebook would use the If statement.password = facebook_hash(input_password) if password == hash_password print (‘Login successful.’) Else print (‘Login failed. Incorrect password.’)The above code just gives a high-level implementation of If statement in the Facebook ID login example used. Facebook hash () function takes the input password as a parameter and compares it with the hash value stored for that user
For Statement
The for statement supports repeated execution of a statement or block of statements that is controlled by an integrable expression. Syntax of For statement:for target in integrable: statement (s)
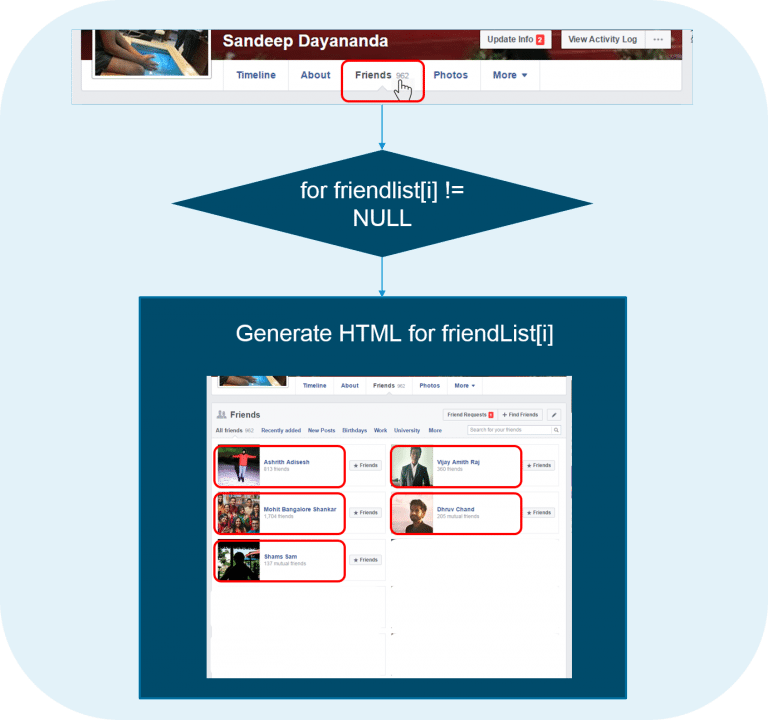
Figure: Python Programming Language- For – Facebook Friends Example
The ‘for’ statement can be understood from the above example.- Listing ‘Friends’ from your profile will display the names and photos of all of your friends
- To achieve this, Facebook gets your ‘friend list’ list containing all the profiles of your friends
- Facebook then starts displaying the HTML of all the profiles till the list index reaches ‘NULL’
- The action of populating all the profiles onto your page is controlled by ‘for’ statement
travelling = input(“Are you travelling? Yes or No:”) while travelling == ‘yes’: num = int(input(“Enter the number of people travelling:”)) for num in range(1,num+1): name = input(“Enter Details \n Name:”) age = input(“Age:”) sex = input(“Male or Female:”) print(“Details Stored \n”,name) print(age) print(sex) print(“Thank you!”) travelling = input(“Are you travelling? Yes or No:”) print(“Please come back again.”)The output is as below: Are you travelling? Yes or No: Yes Enter the number of people travelling:1 Enter Details Name: Harry Age:20 Male or Female: Male Details Stored Harry 20 Male Thank you Are you travelling? Yes or No: No Please come back again.
While Statement
The while statement in Python programming Language supports repeated execution of a statement or block of statements that is controlled by a conditional expression. Syntax of While statement:while expression: statement (s)

Figure: Python Programming Language – While – Facebook Newsfeed Example
We will use the above Facebook Newsfeed to understand the use of while loop.- When we login to our homepage on Facebook ID, we have about 10 stories loaded on our newsfeed
- As soon as we reach the end of the page, Facebook loads another 10 stories onto our newsfeed
- This demonstrates how ‘while’ loop can be used to achieve this
count = 0 print(‘Printing numbers from 0 to 9’) while (count<10): print(‘The count is ‘,count) count = count+1 print(‘Good Bye’)This program prints numbers from 0 to 9 using the while statement to restrict the loop till it reaches 9. The output is as below: The count is 0 The count is 1 The count is 2 The count is 3 The count is 4 The count is 5 The count is 6 The count is 7 The count is 8 The count is 9
Break Statement
The break statement is allowed only inside a loop body. When break executes, the loop terminates. If a loop is nested inside other loops, break terminates only the innermost nested loop. Syntax of Break statement:while True: x = get_next() y = preprocess(x) if not keep_looking(x, y): break process(x, y)

Figure: Python Programming Language- Break – Alarm and Incoming Call
The ‘break’ flow control statement can be understanding from the above example.- Let us consider the case of an alarm on a mobile ringing at a time.
- Suppose the phone gets an incoming call in that time the alarm is ringing; the alarm is stopped immediately, and the phone ringer starts ringing.
- This is how break essentially works.
for letter in ‘The Quick Brown Fox. Jumps, Over The Lazy Dog’: if letter == ‘.’: break print (‘Current Letter :’, letter)This program prints all the letters in a given string. It breaks whenever it encounters a ‘.’ or a full stop. We have done this by using Break statement. The output is as below.
- Current Letter: T
- Current Letter: h
- Current Letter: e
- Current Letter :
- Current Letter: Q
- Current Letter: u
- Current Letter: I
- Current Letter: c
- Current Letter: k
- Current Letter :
- Current Letter: B
- Current Letter: r
- Current Letter: o
- Current Letter: w
- Current Letter: n
- Current Letter:
- Current Letter: F
- Current Letter: o
- Current Letter: x
Continue Statement
The continue statement is allowed only inside a loop body. When continue executes, the current iteration of the loop body terminates, and execution continues with the next iteration of the loop. Syntax of Continue statement:for x in some_container: if not seems_ok(x): continue lowbound, highbound = bounds_to_test() if x<lowbound or x>=highbound: continue if final_check(x): do_processing(x)
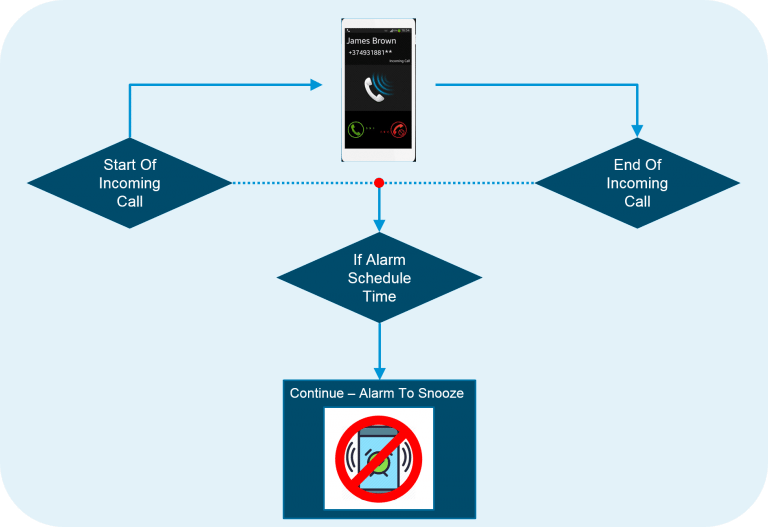
Figure: Python Programming Language – Continue – Incoming Call AndAlarm Example
Example: The Continue statement can be understand using incoming call and an alarm.- Let Suppose we are on a call and the alarm is scheduled during the call time, then the alarm trigger recognizes the call event
- Once the call event is noted and the phone continues the alarm to ring at the next snooze period.
for num in range(10, 21): if num % 5 == 0: print (“Found a multiple of 5”) pass num = num + 1 continue print (“Found number: “, num)This program prints all the numbers except the multiples of 5 from 10 to 20. The output is as follows. Found a multiple of 5 Found number: 11 Found number: 12 Found number: 13 Found number: 14 Found a multiple of 5 Found number: 16 Found number: 17 Found number: 18 Found number: 19 Found a multiple of 5
Pass Statement
The pass statement, which performs no action, can be used as a placeholder when a statement is syntactically required but you have nothing specific to do. Syntax of Pass statement:if condition1(x): process1(x) elif x>23 or condition2(x) and x<5: pass elif condition3(x): process3(x) else: process_default(x)Now let us look at a sample program in Python program to demonstrate the Pass statement.
for num in range(10, 21): if num % 5 == 0: print (“Found a multiple of 5: “) pass num++ print (“Found number: “, num)This program prints the multiples of 5 with a separate sentence. The output is as follows. Found a multiple of 5: 10 Found number: 11 Found number: 12 Found number: 13 Found number: 14 Found a multiple of 5: 15 Found number: 16 Found number: 17 Found number: 18 Found number: 19 Found a multiple of 5: 20 After learning the above six flow control statements, let us now learn what functions are
Functions
Functions in Python programming Language is a group of related statements that performs a specific task. Functions make our programs more organized and help in code re-usability.
Figure: Python Programming Language Understanding Functions
Uses of Functions:- Functions help in code reusability
- Functions provide organization to the code
- Functions provide abstraction
- Functions help in extensibility

Figure: Python Programming Language – Demonstrating The Uses Of Functions
The code used in the above example is as below:# Defining a function to reverse a string def reverse_a_string(): # Reading input from console a_string = input(“Enter a string”) new_strings = [] # Storing length of input string index = len(a_string) # Reversing the string using while loop while index: index -= 1 new_strings.append(a_string[index]) #Printing the reversed string print(”.join(new_strings))
We have thus shown the power of using functions in Python Programing Language.
So this concludes our Python Programming blog. I hope you enjoyed reading this blog and found it informative. By now, you must have acquired a sound understanding of what Python Programming Language is. Now go ahead and practice all the examples. To get in-depth knowledge on Python Programming language along with its various applications, you can enroll here for training Today.